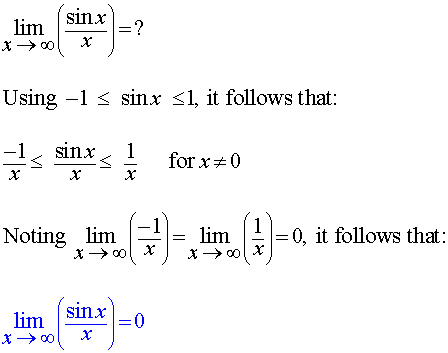Squeeze Theorem for Limits
The Squeeze Theorem asserts that if
two functions approach the same limit at a point, and if a third
function is "squeezed" between those functions, then the third function
also approaches that limit at that point. Formally, the Squeeze
Theorem may be written as:
If g(x) ≤ f(x) ≤ h(x) and lim g(x) = lim h(x) = L, then lim f(x) = L
Example:
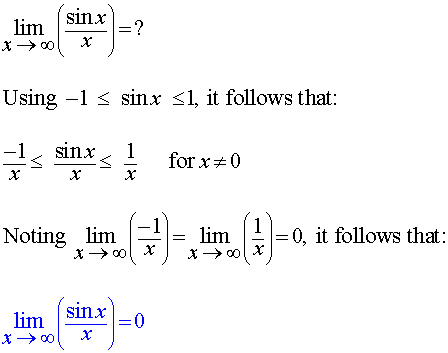
Example: