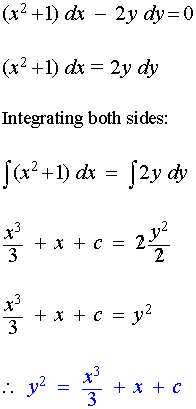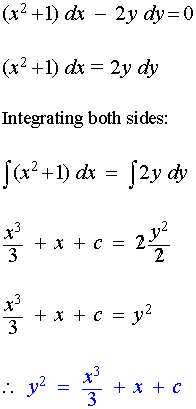Separable First-Order Differential Equations
A differential equation is separable if the variables can be separated:
F(y) dy = G(x) dx
The step towards solving the equation is to integrate both sides:
∫ F(y) dy = ∫ G(x) dx
Remaining step is to solve for y in terms of x (if possible). If it not possible to solve directly for x, the result should be written as an implicit format.
Example:
Solve the equation (x2 + 1) dx − 2y dy = 0
Solution: